Advanced product quality planning (APQP) is a framework of procedures and techniques used to develop products in industry, particularly in the automotive industry. It is similar to the concept of Design for Six Sigma (DFSS).
According to the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG), the purpose of APQP is "to produce a product quality plan which will support development of a product or service that will satisfy the customer." It is a product development process employed by General Motors, Ford, Chrysler, and their suppliers. APQP serves as a guide in the development process and also a standard way to share results between suppliers and automotive companies. APQP specifies three phases: Development, Industrialization, and Product Launch. Through these phases, 23 main topics will be monitored. These topics must be completed before the production is started. They include the following aspects: design robustness, design testing, and specification compliance, production process design, quality inspection standards, process capability, production capacity, product packaging, product testing, and operator training plan.
APQP focuses on:
- Up-front quality planning
- Determining if customers are satisfied by evaluating the output and supporting continual improvement
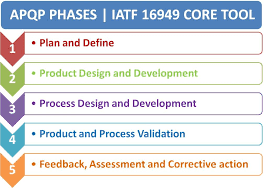
APQP consists of five phases:
- Plan and define program
- Product design and development verification
- Process design and development verification
- Product and process validation and production feedback
- Launch, assessment, and corrective action
The APQP process has seven major elements:
- Understanding the needs of the customer
- Proactive feedback and corrective action
- Designing within the process capabilities
- Analyzing and mitigating failure modes
- Verification and validation
- Design reviews
- Control special/critical characteristics
Useful Links to Read:
01. history-of-total-productive-maintenance
02. why-implement-total-productive
03. what-is-tpm
04. 12-steps-for-tpm-implementation
05. typical-tpm-organizational-chart
06. effectiveness-of-tpm
07. 5-principles-in-tpm-development
08. purpose-and-main-activities-of-kk
09. purpose-and-activities-of-jh-pillar
10. purpose-activity-of-pm-pillar
11. purpose-activities-of-qm-pillar
12. purpose-and-activity-of-dm-pillar
13. purpose-and-activity-of-otpm-pillar
14. purpose-and-activity-of-e-pillar
15. purpose-and-activity-of-she-pillar
16. company-wide-tpm
17. jishu-hozen-information
18. ishu-hozen-equipment-deterioration
19. role-of-production-maintenance-in-jh
20. jishu-hozen-step-1
21. 1s-2s-implementation
22. jh-step-01-abnormalities
23. exposing-seven-types-of-abnormality
24. 2-unfulfilled-basic-condition
25. 3inaccessible-places
26. 4-contamination-sources
27. 5-quality-defect-sources
28. 6-unnecessary-non-urgent-items
29. 7-unsafe-places
30. jishu-hozen-step2
31. jishu-hozen-step-3
32. one-point-lesson-opl
33. visual-control-visual-management
34. 35. what-is-smed
36. why-energy-conservation
37. mobile-phone-handling-important-tips
38. kaizen-way-of-life
39. what-is-kaizen
40. techniques-used-in-kaizen
41. tmv-mba-project-guideline
42. gdmm-project-guidelines
43. importance-of-energy-conservation
44. global-warming-25-tips
45. latest-abcd-from-nursery-school
46. world-environment-day-5th-june
47. be-proud-to-be-engineer-happy
48. lean-tools-hidden-waste
49. waste-over-production
50. wastes-of-defects-rework
51. waste-of-motion
52. Wastes of Transportation
53. 2014 FIFA World Cup Brazil
54. Self Confidence Vs Over confidence
55. How to build self confidence-Hard Work